Our services
Hatha Yoga Module
Ancient concept of Hatha yoga – Different people use yoga for different purposes and different yogas like Bhakthi yoga, Karma yoga, Gnana yoga, Raja yoga and Hatha yoga. To attain Moksha (reach heaven after death), to attain super natural powers, and to attain jeeven samadi. .
Modern concept: Hatha Yoga is the integration of personality at all levels of physical, mental, social, emotional and spiritual. In short each individual to attain good health and to combat modern ills like Diabetes, B.P., Constipation, Insomnia, Tension, worries, anxiety and etc. Hatha Yoga- module is most convenient to use. It consist of some selected asanas and pranayama.
Need of good personal health: Every individual need good health to perform day’s work successfully without getting tired and reserve some energy for next day’s work. This is very important to lead holistic life and longevity. There are different ways to maintain normal personal health. But for various reasons many may not find an opportunity to make use of games or other forms of physical activity to derive health benefits. Yoga can be practiced at home without any equipment.
Features of Hatha yoga module: Depending participants age and sex select any six Asanas suitable to different body parts from among – Padmasan, Bujangasan, Pachimuthanasan, Andha-salabasan, Salabasana, Savasan, Ardha-matsendrasan, Dhanurasan, Sarvangasan, Vepareetakarni, Sirshasan, Halasan Yoga mudra and Pranayama. ( Kapalabhati – cleansing digestive organs and Meditation shall be dealt at a later stage)
There are four stages to perform each Asana: Approach Phase, Asana phase, Holding final position and Reversal Phase. While practising Asanas one should strictly follow yoga sutras to benefit maximum results mentioned at the end. Slow and study movement with ease, and without jerks, normal breathing except Ardha – Salabasan. Focus on any object while performing Asanas.
Note: More importantly: regular practice with conviction, faith, confidence and self-discipline to reap benefits.
-2-
1. PADMASANA: This pose is called Padmasana because it is imitation of the flower lotus as hands and feet are arranged like flower Padmam. The student take his seat with legs fully stretched forward. Then bends his right leg by folding right knee joint and places on the left thigh. Similarly place left leg on right thigh. Keep your trunk and head erect and eyes are focused on the tip of the nose. Keep extended hands on respective knees by keeping thumb and middle fingers together. Maintain this position for one minute and slowly release step by step legs and hands to the starting position. People who may not able to perform the above due to age, stiffness of their concerned joints may keep bent cross legs on the floor and rest of the position as above. Maintain normal breathing.
Advantages: During asana the lower extremities greatly contracted and pressed, and this cause interfere with normal circulation to legs but the pelvic region gets larger blood supply as well as coccygeal and sacral nerves tones up.
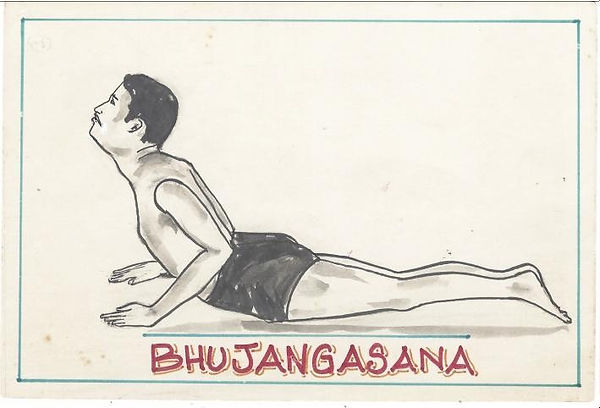
2.BHUJANGASAN OR COBRA POSE: This pose is called Bhujangasan because it gives the appearance of a Cobra snake hood. Final position is like Cobra raising head. The student lies on prone position with relaxed body and mind by fore head touching ground. keeps his bent hands either side of the chest. Now slowly look forward raise chest upward by bending the trunk and maintain Snake hood position. Maintain final position for one minute. Slowly come back to the starting position. Normal breathing.
Advantages: During this positon abdominal muscles are stretched and intra- abdominal pressure is greatly increased. The lumbar, thoracic and cervical regions of the vertebral column are exercised. Back muscles are alternately contracts and relaxes. Concerned muscles & nerves keep the spine elastic and blood circulation increases which is somewhat slow to this parts during normal. If there is any slight displacement in the spinal column, it is adjusted to the normal condition.
-4-
3.SAVASANA: The pose is called savasan, as it requires complete relaxation of body and mind as in the case of a dead person. The technique of this asana is simple to understand, but somewhat difficult to practice. Starting supine position (lying on back.) After deep body and mind relaxation focus (concentrate) on particular object. or concentration on forehead. Eyes are to be kept closed during the process. This asana should be done after every asana as rest to body and mind.
Advantages: Muscles become more efficient, venous blood circulation promoted throughout body and the nervous system is toned up because of relaxed muscles & nerves. Improves concentration as well as prelimenary for Medition.
4.ARDHA-SALABHASANA: Starting prone position. Straight arms by the side of body, palms facing down on the ground, shoulders touching ground, look upward by placing the chin on the ground. Extend the ankle joints. Chin on the ground, From this position raise right leg slowly and steadily back upward. Entire body and left leg touching ground. After one minute come to starting position slowly. From the same position repeat left leg similarly. Hold the breath throughout exercise. Care must be taken to see that no strain is put on the system while performing any asana. It becomes Salabasan when both hands raised simultaneously, which is rather difficult.
Advantages: This exercise is good for pelvic and abdomen.
5.PASCHIMUTANASANA: Starting position- The student takes sitting with extend closed legs forward. He then bends forward, extend hands, catches greater toes with right & left hands respectively. The student then touches knees with face by bending trunk forward slowly and at same time place the elbows by Knees side respectively. Keep legs straight. Care is taken not to allow the knees to bend. Normal breathing. Focus on an object. Maintain the position for one minute. Slowly get back to starting position. Due to stiff joints some people may not be able to reach final position but maintain half the positon. By practice you may be able to reach final position.
Advantages. It is fine stretching exercise to hamstring, back and abdominal muscles. It is remedy for seminal weakness, and also against the possibility of recurrence of sciatica. Blood flow to pelvic organs and lumbosacral part of the spine increases. It also helps to rouse the spiritual force called the kundalini.
6.DHANURASAN: This exercise looks like a Bow. Starting body prone position. Bend both legs back upward, extend hands back and catch ankle joint with same hand same leg. With firm grip at ankle joint raise his trunk, head, look up till the abdomen rests on the ground. You will experience the whole pressure is thrown on abdomen and extremities are fully stretched. Chest raised, head up and look upward. After maintaining the pose for one minute, chest and knees are lowered to the ground. Hands and legs go to starting position. Care must be taken not to sprain joints.
Advantages. Entire body is exercised. There is great amount of contraction and relaxation of muscles, nerves as well as joints. This pose has special benefit to strengthen entire body which cannot be derived from other asanas.
7.Sarvangasan: Starting from body supine position. slowly and gradually lift straight legs up to 30, 45 and 90 degrees till the chest and body rest on shoulders. Support body by placing bent hands on either side of trunk, hands. Shoulders elbow resting on the ground. In this position neck and posterior part of the head resting on floor. Maintain this position for one minute. If a performer unable to do maximum position 90 degrees, go up to 30 degrees by supporting Buttocks with bent hands.
Note : Above is bit difficult, You may try, Half – Sarvangasn or also called as Viparetakarni mentioned below.
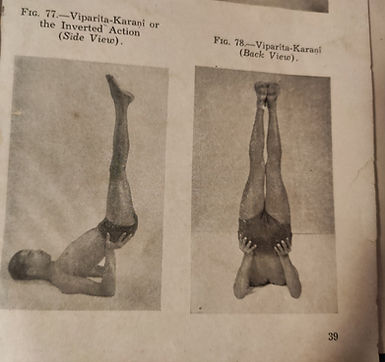
Half Sarvangasan Or Viparetakrni:
Starting body supine position. Slowly lift straight legs up to 30 degrees till the chest and legs rest on shoulders. Support hips and legs by placing bent hands on either side of trunk, hands from shoulder elbow resting on the ground. In this position neck and posterior part of the head resting on floor. Maintain this position for one minute. If a performer unable to do maximum position go up to 90 degrees by supporting buttocks with hands as in Sarvangsan, then practice Vipareetakarine
Advantages. As the body is all most inverted position the Thyroid gland become stronger as the blood circulation increases to neck and head. Symptoms of old age is counteracted by this Asana. Dyspepsia, Constipation, Hernia can be treated through this Asana
8.Ardha Mastsyendrasan: Long sitting position. By bending your right leg place it under between the anus and scrotum. Place your left leg over right thigh bending at the knee, left foot touching ground. Place extended right arm alongside of the left leg, now twist your trunk towards left, look back, move left arm around back try to touch left leg lap. Look back. These movements should take place one after other as smooth and relaxed manner. The main feature of this pose consist in twisting the spinal column. Care should be taken not to strain elbow joint. Throughout practice, student should take care to see that his upper body erect and do not stoop down. Maintain this position for one minute, prolong it later after few days practice. Repeat same movements on right side.
Advantages: Improves spinal flexibility and mobility and helps relieve back pain. Massages the abdominal organs, which can help with digestion and constipation. Calms the mind and nervous system, Can help reduce stress and anxiety and depression. Improves blood circulation by compressing and releasing blood vessels in the torso. Stimulates the liver and kidneys to help flush out toxins and waste products. Strengthens the back and core muscles, Can help improve sleeping patterns
Other benefits: Can help with sciatica, slipped discs, hip joint pain, obesity, and gastritis
9.Yoga Mudhra: is known as symbol of Yoga, From bent leg position, lean forward and touch the ground with fore- head by keeping hands folded upon the back as shown in the above diagram. Mudhra helps the abdominal organs to be kept in their proper place and also tone up the nervous system in general and lumbosacral nerves in particular. Spiritually prolonged practice helps to rouse the KUNDALINI which is the spiritual energy or force, normally locked up in an abdominal centre (navel point )
Advantages: Yoga mudras Asan massage core organs and tones the abdominal muscles. Stretches the spine, shoulders, and core muscles. Alleviates anxiety, stress, and depression, Improves digestion and can help relieve constipation. Help to prevent lower back pain, sciatica, and shoulder disorders. Stimulate parasympathetic system. Improve circulation in the spine. Help Kundalini energy move up the spine. Enhance flexibility and strength of the spine. Energize sexual organs. Strengthen pelvic region in women
Pranayama: is the fourth item of Hatha Yoga. In the original yoga literature, there are four varieties of breathing. We follow the most simple and effective method of breathing called Anuloma- Veloma. This is done from Padmasan position or sitting on a chair, keeping the upper body erect. The method of breathing consist of Inhalation - Retention – Expiration. In Sanskrit is known as Purak- Kubhak–Reshak. Controlled breathing. Breath in- slowly, steadily, uniformly for 10 seconds. When the lungs are filled - retain the air in the lungs for 10 seconds. Breath out the same controlled manner for 10 seconds. This is one breath. Repeat similar 10 breaths. It is to be remembered carefully that Pranayama not merely breathing in and out. It is an attempt to control and direct energy to vital organs. Therefore it is a specialized art be practiced close guidance of an expert. Book reading alone my help much. Advantages: Increase efficient functioning of respiratory and blood circulation.
Important Principles to be remembered while practising Asanas.
-
Asanas should be don slowly and smoothly.
-
When final position of Asana reached, it should be retained for some time with least efforts.
-
While performing Asana concentrate on an object.
-
Asanas should be released slowly and smoothly as it was built.
-
Yogic exercises should commence minimum one hour after food with moderate quantity.
-
Calm and well ventilated place may be used for Yogic exercises.
-
Yoga mat or carpet enough to accommodate length and breadth of the individual to be used to perform Asanas.
-
Duration of final position o every asana depends person to person.
-
After sever illness, Yogic exercises should be undertaken when the patient recovers sufficient energy for their practice.
-
It is postural pattern that is important than reaching final position[BRR1] .
-
Asanas are better gone through in the evening as muscles are more elastic than in the morning.
-
Cold water bath is preferred after performing Asanas.
-
Under no circumstance should exercise lead to longer. Student come out of practice fully refreshed.
-
There no harm in undergoing yogic exercises and strenuous muscular exercise with minimum gap between of two hours.
-
Well balanced sattvic diet is advisable. Sprouted grains, fruits, vegetables Cheese, Raise, Chapattis, in a limited manner.
-
Avoid or minimise smoking and alcohol Reference: Asanas and Pranayama by Swamy Kuvalayananda, Kaivalyadhama, Lonavala, Pune. M.S.India.
[BRR1]